Products You May Like
Details have emerged about a high-severity security vulnerability impacting Service Location Protocol (SLP) that could be weaponized to launch volumetric denial-of-service attacks against targets.
“Attackers exploiting this vulnerability could leverage vulnerable instances to launch massive Denial-of-Service (DoS) amplification attacks with a factor as high as 2200 times, potentially making it one of the largest amplification attacks ever reported,” Bitsight and Curesec researchers Pedro Umbelino and Marco Lux said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
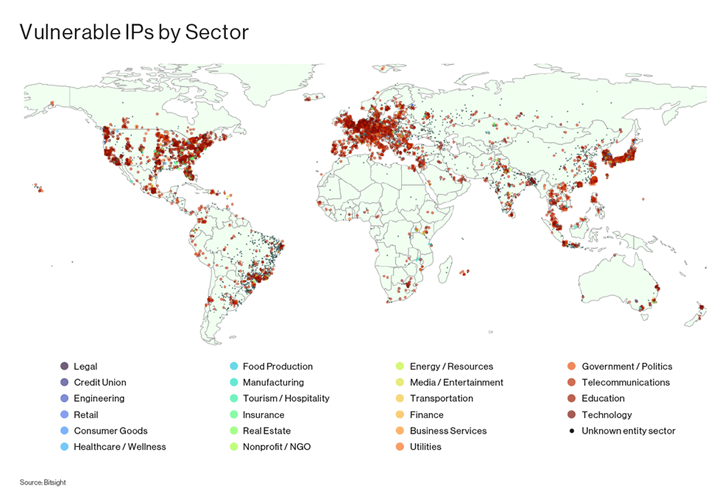
The vulnerability, which has been assigned the identifier CVE-2023-29552 (CVSS score: 8.6), is said to impact more than 2,000 global organizations and over 54,000 SLP instances that are accessible over the internet.
This includes VMWare ESXi Hypervisor, Konica Minolta printers, Planex Routers, IBM Integrated Management Module (IMM), SMC IPMI, and 665 other product types.
The top 10 countries with the most organizations having vulnerable SLP instances are the U.S., the U.K., Japan, Germany, Canada, France, Italy, Brazil, the Netherlands, and Spain.
SLP is a service discovery protocol that makes it possible for computers and other devices to find services in a local area network such as printers, file servers, and other network resources.
Successful exploitation of CVE-2023-29552 could allow permit an attacker to take advantage of susceptible SLP instances to launch a reflection amplification attack and overwhelm a target server with bogus traffic.
To do so, all an attacker needs to do is find an SLP server on UDP port 427 and register “services until SLP denies more entries,” followed by repeatedly spoofing a request to that service with a victim’s IP as the source address.
Zero Trust + Deception: Learn How to Outsmart Attackers!
Discover how Deception can detect advanced threats, stop lateral movement, and enhance your Zero Trust strategy. Join our insightful webinar!
An attack of this kind can produce an amplification factor of up to 2,200, resulting in large-scale DoS attacks. To mitigate against the threat, users are recommended to disable SLP on systems directly connected to the internet, or alternatively filter traffic on UDP and TCP port 427.
“It is equally important to enforce strong authentication and access controls, allowing only authorized users to access the correct network resources, with access being closely monitored and audited,” the researchers said.
Web security company Cloudflare, in an advisory, said it “expects the prevalence of SLP-based DDoS attacks to rise significantly in the coming weeks” as threat actors experiment with the new DDoS amplification vector.
The findings come as a now-patched two-year-old flaw in VMware’s SLP implementation was exploited by actors associated with the ESXiArgs ransomware in widespread attacks earlier this year.