Products You May Like
A new information stealer called Stealc that’s being advertised on the dark web could emerge as a worthy competitor to other malware of its ilk.
“The threat actor presents Stealc as a fully featured and ready-to-use stealer, whose development relied on Vidar, Raccoon, Mars, and RedLine stealers,” SEKOIA said in a Monday report.
The French cybersecurity company said it discovered more than 40 Stealc samples distributed in the wild and 35 active command-and-control (C2) servers, suggesting that the malware is already gaining traction among criminal groups.
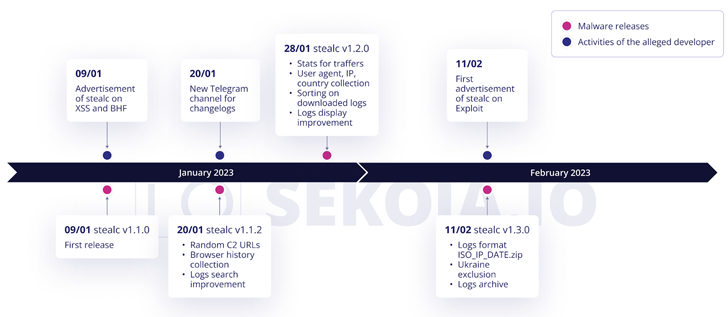
Stealc, first marketed by an actor named Plymouth on the XSS and BHF Russian-speaking underground forums on January 9, 2023, is written in C and comes with capabilities to steal data from web browsers, crypto wallets, email clients, and messaging apps.
The malware-as-a-service (MaaS) also boasts of a “customizable” file grabber that allows its buyers to tailor the module to siphon files of interest. It further implements loader capabilities to deploy additional payloads.
SEKOIA assessed with “high confidence that its alleged developer quickly established itself as a reliable threat actor, and its malware gained the trust of cybercriminals dealing with infostealers.”
Among the distribution vectors used to deliver Stealc are YouTube videos posted from compromised accounts that link to a website peddling cracked software (“rcc-software[.]com”).
This also indicates that users searching for ways to install pirated software on YouTube are a target, mirroring the same tactic adopted by another infostealer dubbed Aurora.
“Since customers of the Stealc MaaS own a build of its administration panel to host the stealer C2 server and generate stealer samples themselves, it is likely that the build will leak into the underground communities in the medium term,” the company added.
According to antivirus vendor Avast, FormBook, Agent Tesla, RedLine, LokiBot, Raccoon, Snake Keylogger, and Arkei (along with its fork Vidar) accounted for the most prevalent stealer malware strains during Q4 2022.